Key Concepts in Artificial Intelligence for Medical Imaging
Explore the main technical concepts behind artificial intelligence applied to dental radiography analysis, from neural networks to semantic segmentation.

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the field of medical imaging, particularly in dentistry. To understand how these technologies work, it is essential to grasp the technical concepts that underpin them.
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are the foundation of most modern image-based AI systems. They are particularly effective at detecting spatial features—such as edges, textures, and shapes—through the use of filters (or kernels) that slide over the input image.
In dental radiography, CNNs help identify relevant anatomical or pathological regions like enamel, dentin, caries, or fillings, by learning hierarchical features from the input images.
🧠 CNNs are the first step in many image analysis pipelines—they extract the features that later models use for tasks like classification or segmentation.
Semantic Segmentation
Semantic segmentation goes beyond classifying an image—it labels every pixel with a category. Instead of just predicting whether a pathology is present, the model outputs a segmentation map that shows exactly where each class is located.
In practice, for dental images, this results in a single segmented mask where each region (e.g., enamel, pulp, caries) is represented by a unique color or pixel value.
You don’t get multiple images—just one mask where each pixel value corresponds to a category.
| Original Image | Segmented Mask |
|---|---|
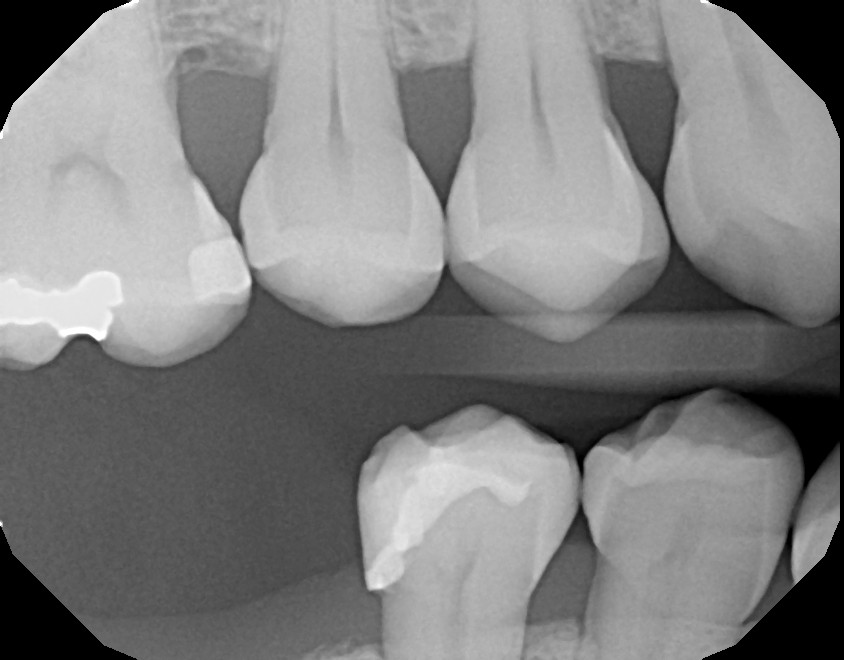 | 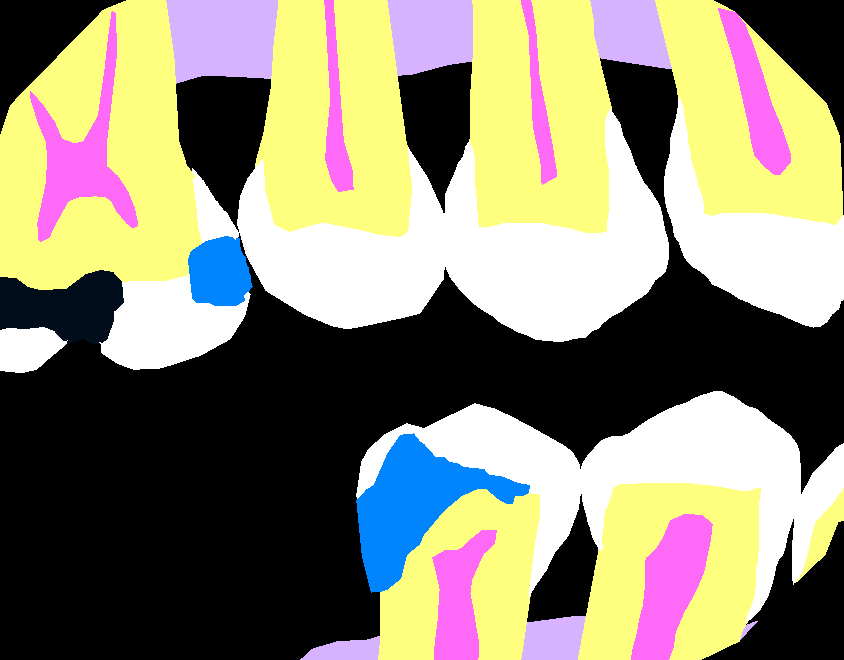 |
These masks are typically color-coded or stored as grayscale images with predefined values (e.g., 0 for background, 1 for enamel, 2 for pulp, etc.).
Why it matters
- Enables pixel-level analysis for precise localization
- Essential for building clinical tools like caries detectors or treatment planning assistants
- Used to generate overlays or heatmaps on radiographs for interpretability
📌 Each mask represents all classes in a single image, not separate masks per class—though in some workflows, binary masks per class can be derived from the master mask.
Data Annotation
To train segmentation models, precise and structured annotations are essential. This process is typically carried out using specialized tools where experts outline structures like enamel, pulp, or caries directly over the images.
🧩 High-quality annotations are the foundation of accurate medical AI models.
Here’s a comparison of popular annotation tools and formats:
| Tool | Annotation Type | Formats Supported | Best For | Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CVAT | Polygon, bounding box, mask | Pascal VOC, COCO, YOLO, LabelMe | Medical image annotation with polygons | cvat.ai |
| Labelbox | Polygon, segmentation, keypoints | COCO, JSON, custom formats | Cloud-based collaborative workflows | labelbox.com |
| SuperAnnotate | Polygon, mask, video | COCO, YOLO, custom JSON | AI-assisted annotation, QA features | superannotate.com |
| MakeSense.ai | Polygon, bounding box | YOLO, Pascal VOC, COCO | Free, browser-based, quick setup | makesense.ai |
Common Annotation Formats
| Format | Description |
|---|---|
| Pascal VOC | XML-based format with bounding boxes and segmentation masks. |
| COCO | JSON-based format supporting instance and semantic segmentation. |
| LabelMe | JSON format for polygons and object classes, commonly used in academia. |
| YOLO | TXT-based format focused on real-time object detection (less common in medical). |
These tools enable consistent and detailed labeling, crucial for building datasets that allow neural networks to learn effectively.
Advanced Architectures
U-Net
Designed for medical segmentation, the U-Net architecture is highly efficient when working with images that require pixel-level precision. Its "U" shape allows it to capture both global context and fine details simultaneously.
ResNet
Residual Networks (ResNet) enable the construction of deep models without degradation. They are highly robust and combine well with other architectures.
Often used together: a U-Net with ResNet as an encoder yields excellent results in medical tasks.
Model Training
Training typically occurs on platforms like Google Colab, using frameworks such as PyTorch or TensorFlow. The process involves:
- Loading images and masks (e.g.,
BW_00001.jpegandBW_00001.jpeg_Enamel_mask.png). - Defining the architecture (U-Net, ResNet, DeepLab, etc.).
- Tuning the parameters and evaluating metrics such as
IoUorDice Score.
Chatbots and RAG in Healthcare
The RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) technique combines text generation (like ChatGPT) with real databases or medical documents. This allows for the creation of explanatory chatbots that can answer questions about treatments, diagnoses, or medical processes based on evidence and real articles.
In clinical settings, a well-trained chatbot can assist both patients and professionals.
Real-World Application at DENTREAD
At DENTREAD, we combine these technical approaches with clinical expertise to:
- Precisely annotate images in a categorized manner.
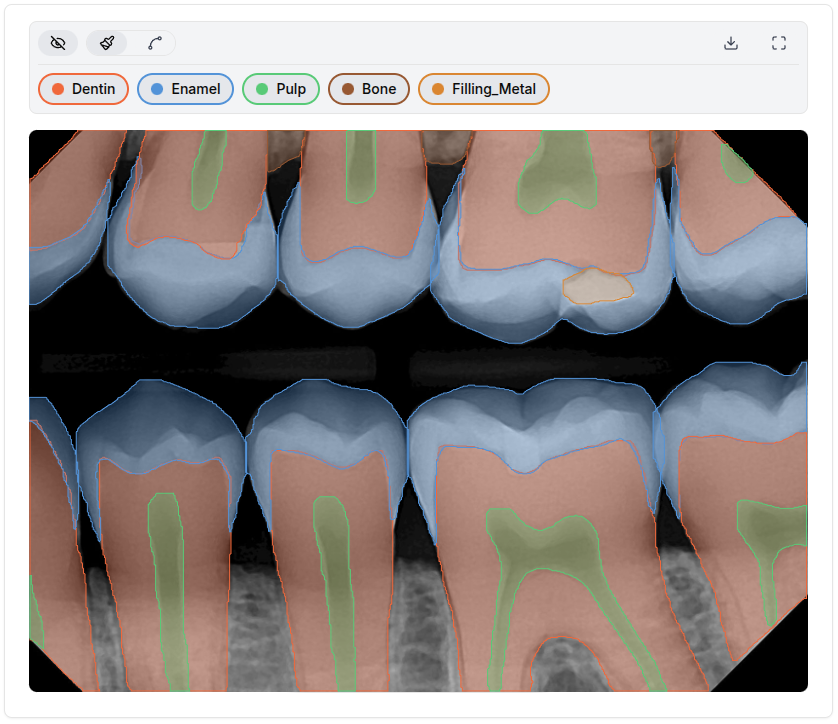
- Train multi-class segmentation models for dental structures such as:
EnamelDentinPulpCariesCrown_MetalFilling_MetalFilling_Non-MetalRoot Canal Obturation
- Integrate explanatory chatbots using real data to improve communication with patients.
Conclusion
Understanding these concepts is crucial for advancing medical AI. It is not just about models, but about building reliable, explainable, and human-centered tools.
